다운타임을 최소화하는 메이저 버전 업그레이드
무엇이 메이저 버전 업그레이드인가
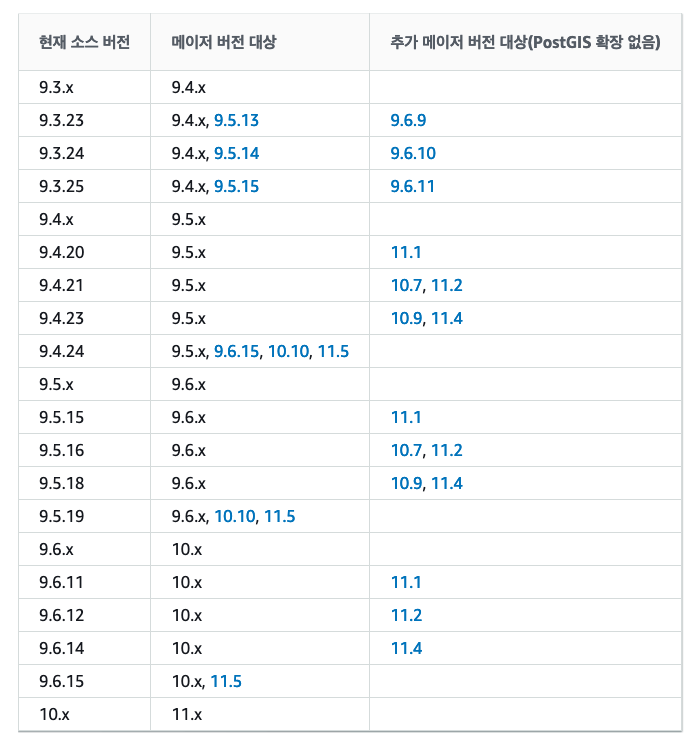
메이저 버전을 업그레이드 하는 방법은 크게 3가지 방법이 있고 PG 개발그룹(PGDG)에서도 이 3가지 방법을 권고하고 있다.
- pg_dumpall
- pg_upgrade 👈 이번에 다루는 방법
- via Replication
pg_dumpall (or pg_dump)
특징 및 주의점
- Logical 백업 방식
- Plain Text SQL문으로 백업
- 클러스터 or 데이터베이스 레벨로 백업
- 데이터베이스 레벨로 백업을 하고자 할 때에는 pg_dump 사용
- 데이터베이스 레벨로 스키마 변경 없이 단순히 덤프만 받을 때는 pg_dump -Fc 옵션을 사용하면 덤프 파일 용량이 4배~7배 가량 줄어듬
- 100GB 이하 급의 작은 클러스터에 적합
- 상위 버전의 pg_dumpall/pg_dump를 이용하고 pg_dump의 full path 명시하여 실행
단점
- 데이터베이스가 크면 클수록 다운타임도 더 필요하고 그 시간을 예측하기가 어려움
- 따라서 수백 GB급 또는 TB 이상의 사이즈인 클러스터를 대상으로는 최선의 옵션이라고 보기 어려움
- as-is, to-be 이중으로 스토리지 공간이 필요함

pg_dumpall 방식으로 진행하는 경우의 대체적인 작업 타임라인
pg_upgrade
EDB사에서 공식적으로 발표한 pg_upgrade로 업그레이드가 불가능한 경우 - 제한사항(Limitations)
- data directory가 NFS 파일시스템을 사용하는 경우
- ✔️ 파티션 테이블을 참조하는 Foreign key 제약조건이 존재하는 경우 (특히 9.4 이하 버전에서 SUBPARTITION BY 구문으로 써서 파티션 테이블을 생성했다면 pg_dump & pg_restore를 이용하여 해당 테이블은 따로 복원해줘야 한다)
- 해시 파티션인 경우 pg_upgrade 후에 리빌드가 필요
- 업그레이드 하고자 하는 버전의 EDB 설치
- as-is에서 사용 중인 extension을 파악해두고 to-be EDB에 미리 설치
- ✔️ github 등에 공개된 써드 파티 모듈을 많이 사용하는 경우 새 버전에 대응하는 모듈이 아직 개발되지 않았을 수 있음
- 통상 $PGDATA 환경변수에 지정하는 데이터 디렉토리 이외의 영역에서 테이블스페이스를 사용하는 경우 장애 포인트가 될 수도 있음
- 기존의 postgresql.conf, pg_hba.conf, SSL 설정을 위한 인증키 등은 pg_upgrade -c 체크기능으로 그 오류를 거를 수 없기 때문에 미리 사전작업을 해두어야 함
- initdb로 새 버전의 EDB 클러스터 생성
- -c 옵션으로 as-is와 to-be 간의 호환성 체크
✔️ 3번 단계까지 진행한 후 본격적인 업그레이드 작업을 시작하기 전에 -c 옵션으로 호환성 체크를 해보는 것이 중요.
✔️ 사전 체크를 통과했더라도 pg_upgrade 작업 중에 에러가 있을 수 있으니 최소한의 기준을 통과했다는 정도로 받아들이자.
[enterprisedb@EDB_11_6 data]$ /usr/edb/as12/bin/pg_upgrade -c
Performing Consistency Checks on Old Live Server
------------------------------------------------
Checking cluster versions ok
Checking database user is the install user ok
Checking database connection settings ok
Checking for prepared transactions ok
Checking for reg* data types in user tables ok
Checking for contrib/isn with bigint-passing mismatch ok
Checking for tables WITH OIDS ok
Checking for invalid "sql_identifier" user columns ok
Checking for presence of required libraries ok
Checking database user is the install user ok
Checking for prepared transactions ok
장점
- 링크 모드를 이용하면 다운 타임을 최소화하면서 엔진 업그레이드가 가능
단점
- 소스(source)와 타겟(target) 시스템이 같은 호스트여야 한다
테이블 스페이스 및 더미 데이터 작성
CREATE TABLESPACE tbs_master OWNER enterprisedb LOCATION '/archive/arc_wal/tbs_master';
CREATE TABLE t1 (
id SERIAL CONSTRAINT first_key PRIMARY KEY,
code VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
article TEXT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
department VARCHAR(4) NOT NULL
) tablespace tbs_master ;
insert into t1 (
code, article, name, department
) select
left(md5(i::text), 10),
md5(random()::text),
md5(random()::text),
left(md5(random()::text), 4)
from generate_series(1, 20000000) s(i);
link 방식의 pg_upgrade 실행 결과
old 클러스터 셧다운 후 pg_upgrade 진행
/usr/edb/as11/bin/pg_ctl stop -D /var/lib/edb/as11/data
pg_upgrade -d /var/lib/edb/as11/data -D /var/lib/edb/as12/data -b /usr/edb/as11/bin -B /usr/edb/as12/bin -p 5444 -P 5445 -j 2 --link
Performing Consistency Checks
Checking cluster versions ok
Checking database user is the install user ok
Checking database connection settings ok
Checking for prepared transactions ok
Checking for reg* data types in user tables ok
Checking for contrib/isn with bigint-passing mismatch ok
Checking for tables WITH OIDS ok
Checking for invalid "sql_identifier" user columns ok
Creating dump of global objects ok
Creating dump of database schemas
ok
Checking for presence of required libraries ok
Checking database user is the install user ok
Checking for prepared transactions ok
If pg_upgrade fails after this point, you must re-initdb the
new cluster before continuing.
Performing Upgrade
Analyzing all rows in the new cluster ok
Freezing all rows in the new cluster ok
Deleting files from new pg_xact ok
Copying old pg_xact to new server ok
Setting next transaction ID and epoch for new cluster ok
Deleting files from new pg_multixact/offsets ok
Copying old pg_multixact/offsets to new server ok
Deleting files from new pg_multixact/members ok
Copying old pg_multixact/members to new server ok
Setting next multixact ID and offset for new cluster ok
Resetting WAL archives ok
Setting frozenxid and minmxid counters in new cluster ok
Restoring global objects in the new cluster ok
Restoring database schemas in the new cluster
ok
Adding ".old" suffix to old global/pg_control ok
If you want to start the old cluster, you will need to remove
the ".old" suffix from /var/lib/edb/as11/data/global/pg_control.old.
Because "link" mode was used, the old cluster cannot be safely
started once the new cluster has been started.
Linking user relation files
ok
Setting next OID for new cluster ok
Sync data directory to disk ok
Creating script to analyze new cluster ok
Creating script to delete old cluster ok
Upgrade Complete
Optimizer statistics are not transferred by pg_upgrade so,
once you start the new server, consider running:
./analyze_new_cluster.sh
Running this script will delete the old cluster's data files:
./delete_old_cluster.sh
완료 작업
/usr/edb/as12/bin/pg_ctl start -D /var/lib/edb/as12/data -p 5445
무사히 pg_upgrade가 끝났다면 vacuum을 실행하고 old 데이터 디렉토리를 삭제하는 스크립트가 자동으로 생성된다.
$ /usr/edb/as12/bin/vacuumdb -p 5445 --all --analyze-in-stages
$ ./delete_old_cluster.sh